The traditional medium frequency furnace lining material has three kinds, one is acidic furnace lining, by quartz sand dry pounding molding, binder for borax or boric acid; another is magnesium sand dry pounding molding, binder is also borax or boric acid. The last one is neutral furnace lining, pounding molding by high alumina bauxite clinker. In recent years, with the development of technology, the emergence of a variety of new materials, medium frequency furnace lining materials, there are many new furnace lining materials.
1.Acidic furnace lining
Acidic furnace lining is mainly quartz sand, it is inexpensive, widely distributed, good insulation, low construction requirements, application of defects, production is more stable, but the quartz sand refractoriness is low, on the casting of large intermediate frequency furnaces will not be able to meet the requirements. And there are secondary phase changes in the heating process, poor dimensional stability, chemical stability is not ideal, easy to react with the slag and cause erosion. In order to avoid these shortcomings can be used electrofused quartz, which has a high content of silica content of more than 99%, the refractoriness is significantly improved, close to the melting point, and there is no secondary phase change in the temperature rise, there is no size change in the temperature rise, the thermal shock stability is also greatly improved.
2.Neutral furnace lining
The use of electrofused corundum as a medium frequency furnace lining, due to the white corundum melting point of up to 2050 ℃, hardness of up to eight, wear-resistant, high temperature resistance, chemical stability is also better than quartz. It is suitable for high temperature cast steel or large furnace lining. Characterized by the same phase change and thermal expansion coefficient of the shortcomings of the large, in practice, the addition of spinel micro-powder can significantly improve the erosion resistance and dimensional stability.
3.Alkaline furnace lining
Traditional alkaline furnace lining using magnesium sand dry pounding molding, the advantage is high refractoriness, close to 2800 ℃, the disadvantage is the expansion coefficient is large, easy to crack, magnesium sand furnace lining erosion resistance, long service life, low price, the application is very widely used, the use of the use of adding white corundum micro-powder or spinel micro-powder significantly improve the service life.
4.Spinel furnace lining
Spinel lining is a new type of furnace lining materials, it uses alumina and magnesium oxide molding, high-temperature firing or electrofusion pre-synthesis of spinel, and then according to the requirements of the production of a variety of granular specifications, used as an intermediate frequency furnace lining, the bonding agent is still used borax or boric acid, which has the advantages of white corundum lining, magnesium sand lining, and to avoid the shortcomings of its lining is a large-scale medium-frequency furnace lining and high-temperature furnace lining of the direction of development. Many imported furnace lining materials belong to this type.
5.Furnace lining materials, new technology, new materials
①Adding ultrafine powder (mostly in a few microns) to the traditional furnace lining materials can improve the erosion resistance and thermal shock stability of the furnace lining materials, such as silica micropowder, alumina micropowder, white corundum micropowder, spinel micropowder and so on.
② Dry molding. Traditional furnace lining are used dry powder dry pounding molding, the disadvantage is easy to stratification, resulting in voids and other defects. Semi-dry method of adding 2% to 3% water mixing, reduce lamination, good integrity, will not cause too much harm, only low-temperature baking time a little longer.
③ Semi-dry molding to join the pure calcium aluminate cement, with pure acidic or neutral lining; and in the alkaline lining to add magnesium oxide, sodium hexametaphosphate and so on.
Formulation and proportioning of the furnace lining material, the furnace lining material must have the following physico-chemical properties:
(1) High refractoriness steel melting temperature of 1500 ~ 1700 ℃, the furnace lining material must be able to withstand high temperatures for a long time without melting.
(2)Small coefficient of linear expansion and volume expansion in the sintering process furnace lining materials will produce thermal expansion and contraction, too much expansion or contraction will cause cracks in the sintered layer. Adding boric acid will reduce the rate of volume change and linear shrinkage of quartz electric furnace, reducing the chance of cracks.
(3) Good rapid cooling and heating in the use of the furnace lining is periodically heated and cooled, accompanied by thermal expansion and contraction of the furnace will produce stress to cracking. Furnace lining materials good resistance to rapid cooling and heating is to avoid cracks in the material is an important characteristic. Factors affecting the good or bad rapid cooling and heating of the furnace lining are the ratio of sand particles, knotting density, and the expansion coefficient of the refractory material. Therefore, appropriate increase in the particles and large particles of refractory materials, increase the density of knotting, the choice of expansion coefficient of small materials will be good to get a good resistance to rapid cooling and heating of the furnace lining.
(4) Resistant to slag erosion.
(5) Good insulation between the metal in the furnace and the inductor has tens to hundreds of volts potential difference, the furnace lining materials must have sufficient insulation to avoid breakdown. Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 and other ferromagnetic substances can significantly reduce the insulation, must be carefully selected to improve the purity of the furnace lining materials.
There are three types of electric furnaces based on the chemical properties of the lining material:
1)Alkaline electric furnace, made with CaO, MgO, ZrO2, BeO, ThO2, etc., of which MgO is the most commonly used, and other refractories with high price are seldom used;
2)Acidic electric furnace, made with SiO2;
3) neutral electric furnace, made of graphite; Al2O3-MgO; Al2O3-ZrO2-SiO2, mostly used for smelting high alloy materials.
Formulation of furnace lining materials
1.Sand ratio
There are roughly three grades of sand used for lining knots, coarse sand (2 to 6) mm, high melting point, about 20% to 25%. In the furnace lining plays a skeleton role. Coarse sand proportion is too high will reduce the furnace winding performance and strength, appropriate to improve the proportion of coarse sand is conducive to improve the lining of the rapid heat and cold resistance, reduce the possibility of cracks.
Sand particles (0.5 ~ 2.O) mm about 25% ~ 30%, the role of sand particles is to fill the gap between the coarse sand to increase the density of stacking, improve sintering performance, improve strength.
Fine sand particles less than 0.5mm accounted for about 40% to 50%, it fills the gap between the coarse and medium sand particles. Its melting point is slightly lower, the first sintering by the boric acid melting and will be coarse and medium sand grains bonded together, so it can improve sinterability, improve the density.
2.Fluxes
Under normal circumstances, the sintering temperature of MgO sand 1750 ℃, quartz sand sintering temperature 1450 ℃, if you do not add anything to sinter these refractory materials is very difficult, in order to improve the sintering of high temperature refractory sand particles must be added to the flux boric acid (H3BO3), dehydrated to B203, (1000 ~ 1300) ℃ when the B203 and sand materials in the CaO, MgO, Si02, etc. form low melting point compounds: MgO-B2O3 1142 ℃, 2MgO-B2O3 1342 ℃, 3MgO-B2O3 1366 ℃, SiO2-B2O3 1200 ℃, CaO-B2O3 970 ℃. These low melting point compounds bond the loose sand grains into a structurally dense sintered layer with sufficient strength.
The amount of boric acid added according to the furnace lining materials, steelmaking with alkaline furnace plus (0.8% ~ 1.5%) H3BO3, non-vacuum furnace take (1.2% ~ 1.5%) H3BO3, vacuum furnace with (0.8% ~ 1.2%) H3BO3; acidic furnace with (1.5% ~ 2.0%) H3BO3 to join the steel lining, smelting cast iron, acidic furnace take 0% ~ 2.5%. Pay attention to control the amount of boric acid added, because every 1% H3BO3 make quartz sand melting temperature drop 15 ~ 20 ℃, this effect will damage the service life of the furnace.
3.Furnace lining material structure
Sintered lining is not a uniform whole, due to the inner layer of the lining temperature is the highest outer layer of the lowest temperature, from inside to outside to form a temperature gradient, the innermost layer for the fully sintered layer, the middle of the semi-sintered layer, the outermost layer for the loose layer. This structure is very favorable to improve the rapid cooling and heating and reduce heat loss.
4.Knotting
In order to make the bulk sand into a certain density of the furnace lining, must be carefully pounded. Small furnaces can be manually knotted with tools, while large furnaces are knotted with a vibrating furnace builder. Furnace machine using an air motor to produce 1.3 × 10t times per second vibration, resulting in 3-5kg/cm2 vibration force.
Extra-large furnaces do not use the knotting method of molding, but with special refractory bricks masonry furnace, refractory materials are mostly alkaline refractory bricks.
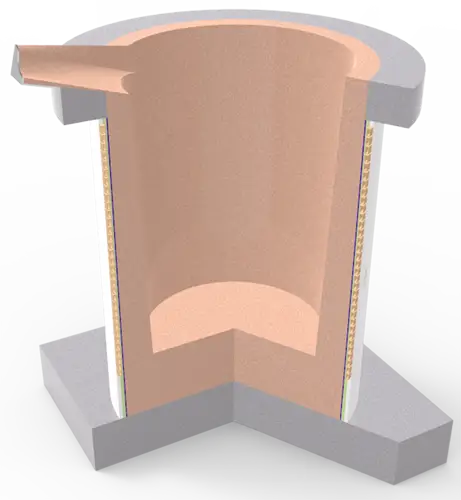
Induction Furnace
