The design of the electric furnace and the configuration of the refractory material for the furnace lining affect the operating life of the converter. The following is a description of the design of the furnace roof, cylinder and hearth as well as the configuration of the refractory material for the lining of the furnace.
1.Furnace top
The roof of electric furnace is a section of arc shape. The mass of the roof of the electric furnace is large, for the 5t brick electric furnace, the mass of the roof is close to 5t; for the water-cooled cover, some of them are more than 10t. Electric furnace roof center part of the small cover to take prefabricated blocks, or water-cooled, half-water-cooled cover. Electric furnace cover is subject to both high temperature, and often subject to the temperature from high to low temperature of the dramatic change in the role of the refractory material requirements are high.
At the beginning of the main brick cover with silicon, its refractoriness between 1690 ~ 1710 ℃, with the increase in the intensity of electric furnace smelting, furnace temperature increases, coupled with silicon brick resistance to rapid cooling and rapid heat and resistance to alkaline slag erosion ability is poor, silicon brick roof can not meet the requirements.
At present, most of the use of good cold and heat resistance, refractoriness of 1750 ~ 1790 ℃ high alumina bricks to build the furnace cover. High-alumina bricks in use is the disadvantage of high temperature on the lime powder and alkaline slag containing iron oxide resistance is poor, the brick body in the role of lime powder and iron oxide, layer by layer flaking, and even melting, into the slag will also make the slag become very thin. Therefore, some factories have been used in higher refractoriness (at 2100 ℃ or so), resistance to alkaline slag stronger aluminum and magnesium bricks to build the main part of the furnace cover, only in the electrode holes and charging holes near the high alumina bricks are still used. The roof of the ultra-high-power furnace is water-cooled, and the small electrode cover is made of high alumina prefabricated blocks with water-cooled outer ring.
In addition, the use of brick masonry vault of the inner surface is smaller than the outer surface, so that can be used on the large and small wedge-shaped brick masonry, brick and brick wedged tightly with each other, so that the arch of the greater stability. In smelting practice, with electrode holes in the central part of the cover life of the lowest, with a certain degree of arch, so that the central part of the furnace from the high temperature zone farther is also conducive to improving the life of the cover. But this arch can not be overly high, otherwise in the steel, the roof brick will be easy to turn down.
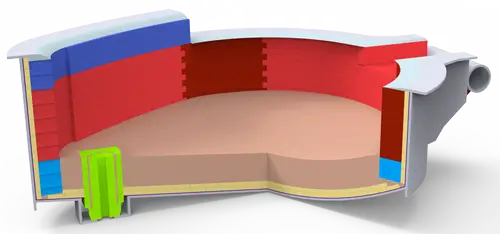
2.Furnace cylinder
Electric furnace used to contain crude steel lower part of the furnace is called the furnace cylinder. Furnace cylinder of the electric furnace is generally spherical and conical joint shape, the bottom is spherical, the melt pool for the truncated cone, the side of the cone and the plumb line into 45 °, the height of the spherical bottom is about 20% of the total depth of the liquid steel. The role of the spherical bottom is easy to gather steel at the beginning of melting, not only to protect the bottom of the furnace, to prevent the arc in the bottom of the furnace directly in contact with the refractory material, but also to accelerate the melting, so that the slag covering the liquid steel to reduce the liquid steel suction cooling, the side of the conical part of the plumbline and the 45 °, to ensure that the electric furnace tilt 40 ° or so can be out of the steel out of a clean, and is conducive to the operation of the hot repair of the lining.
3.Furnace chamber
The hearth of the electric furnace is the part of the electric furnace above the furnace cylinder, which is composed of the water-cooling disk. The hearth of the electric furnace is an important area to satisfy the charging of the electric furnace and complete the metallurgical function. The hearth is generally in the shape of a conical table. The inclination angle of the furnace wall is generally between 6°~7°, the inclination of the furnace wall is to facilitate the charging operation. If the inclination angle is too large, the diameter of the furnace shell is increased, the heat loss is increased and the mechanical devices have to be enlarged. The height of the furnace chamber refers to the electric furnace molten pool slope plane, that is, the height from the corner of the furnace wall to the upper edge of the furnace shell. The hearth should be kept at a reasonable height to avoid overheating of the top of the furnace and to affect the operation of adding two batches of material. Furnace chamber is too high, the heat loss increases, and the height of the required plant should be increased accordingly. Generally speaking, 5t below the small electric furnace, the hearth height and the hearth of the melting pool diameter ratio of 0.5 ~ 0.6 between the capacity of 10 ~ 40t electric furnace, the hearth height and the hearth of the melting pool diameter ratio of 0.45 ~ 0.5 between the 80 ~ 180t electric furnace in the 0.4 ~ 0.45 between. As the capacity of the electric furnace increases, the relative height decreases in order to shorten the length of the electrode and the length of the busbar to reduce the resistance and impedance, as well as to reduce the height of the plan.
More details about EAF Furnace
How does an EAF furnace work?
In electric arc furnaces, the charge material (the material entered into the furnace for heating, not to be confused with electric charge) is directly exposed to an electric arc, and the current from the electrode terminals passes through the charge material.
What is the difference between EAF and BOF furnace?
While EAF steelmaking relies on electricity and recycled metals, Blast Furnace/BOF depends on raw materials like Iron Ore and Metallurgical Coke as part of a process where oxygen is blown into the furnace at a high velocity.
What is the difference between a blast furnace and an EAF?
Unlike traditional blast furnaces that require coal to generate heat, EAFs operate with electricity, making them more adaptable to energy availability and potentially more environmentally friendly.
What is the basic principle of electric arc furnace?
The electric arc furnace is used to reduce iron from iron ore. Heat is generated from an electric arc between electrodes. Oxygen is blown into the furnace, and lime and other materials are added to combine with the impurities and form slag. Molten iron is extracted and poured out via a tapping spout.
What does EAF mean on a furnace?
An electric arc furnace (EAF) is a furnace that heats material by means of an electric arc, combined with the action of chemical power provided by the use of oxygen and fuel.
What are the different types of EAF?
There are two types of EAFs: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). AC EAFs have three electrodes, while DC EAFs have two: a cathode, which is a single electrode in the roof of the furnace, and an anode in the bottom of the furnace.
